“Yangtze River” Software Architecture: From "Single Point Limitation" to "Global Collaboration" Drive visual inspection intelligent engine!
Date:2025-11-21 Views:348
Based on distributed architecture, break the bottleneck of single point architecture
Taking collaboration as the quality, building a solid foundation for intelligent detection
With the era of rapid development, KEYETECH has gained deep insights into the pain points of the industry based on massive data, independently developed the "Yangtze River" distributed software architecture, and created the concept of "division of labor and collaboration, dedicated personnel doing specialized tasks". Through technological breakthroughs, it provides stable, efficient, and scalable technological upgrades for AI visual inspection.

First break, then stand
The inevitability of distributed computing from the perspective of 'invisible bottlenecks'
In the practical application of AI visual inspection, the shortcomings of traditional software architecture have gradually become a "roadblock" to business promotion:
The data carrier cannot hold up: TB level high-definition quality inspection images continue to be generated, and expansion requires downtime to replace hardware, which cannot adapt to the exponential growth of data volume;
Real time detection of 'unable to withstand': The production line needs to process dozens of frames of images per second, while also carrying "real-time detection+model tuning", which is prone to software crashes, restarts, etc;
Fault response 'unable to keep up':Traditional software architecture integrates storage, computing, and detection services into a single node. Once a failure occurs, a comprehensive investigation is required, which seriously affects production efficiency.

It is precisely these pain points that make the distributed architecture from a single point to collaboration an inevitable choice for upgrading AI visual inspection technology.
“Yangtze River” distributed architecture
Breakthrough in Four Main Dimensions, Reshaping AI Visual Inspection Efficiency
KEYETECH has independently developed a distributed software architecture, named after the "Yangtze River", with the deep intention of hoping that our company's technology system can converge like the Yangtze River, gathering thousands of streams and forming a powerful momentum.
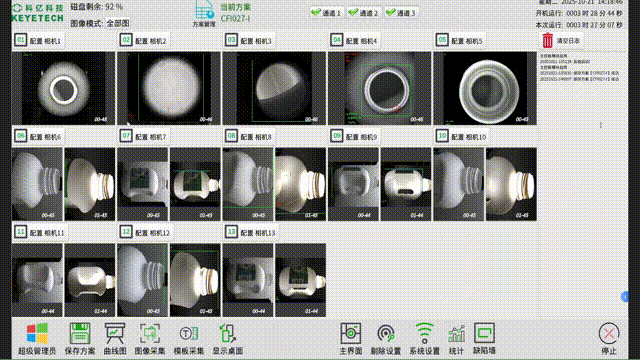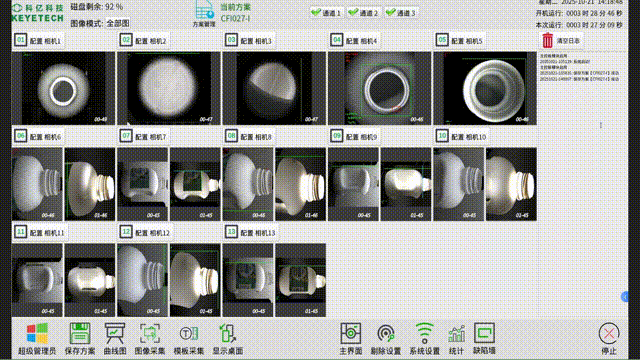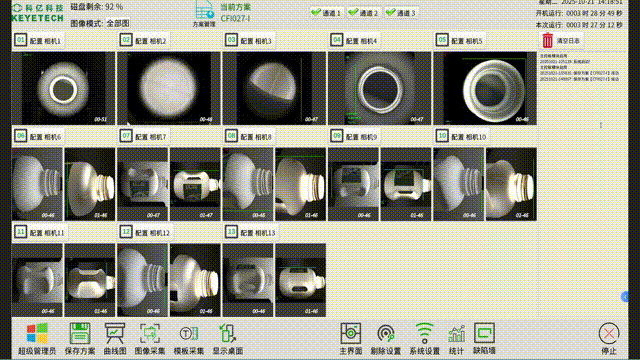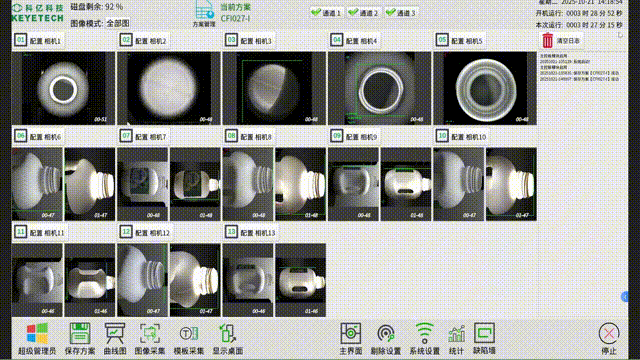
The "Yangtze River" distributed architecture is not simply a "multi node deployment", but a full stack customized solution tailored to the "data intensive, real-time, and fault sensitive" characteristics of AI visual inspection. Its core technological advantages are reflected in four dimensions:
Scalability: Carrying massive amounts of visual data
No need to refactor the system, simply "horizontally increasing nodes" can expand storage and computing capabilities. Architecture seamlessly connects to avoid software crashes and restarts caused by data overflow.
High availability: powerful self-healing and adaptability
The distributed architecture design of "Yangtze River" by KEYETECH is inherently resilient, with no single point of failure (SPOF). Through "data multi replica redundancy", the failure of any node will not cause the collapse of the entire system. If a detection node fails, the system can switch to a backup node within 100ms to ensure uninterrupted quality inspection of the production line.
High fault tolerance: Accurately locate node faults
Relying on real-time node health monitoring and log tracking, the fault location accuracy can reach the level of "IP+service port", without the need for a "comprehensive investigation".
Cloud Integration: Connecting the Entire Link of "Data Computing Application"
The edge end processes the detection task in real time through the self-developed AI edge computing unit, and the cloud distributed node is responsible for data storage and model training. The two work together to achieve the automation of the whole process of "real-time detection - data synchronization - model iteration - deployment update", without manual intervention.
Hardware foundation
AI edge computing unit, making the architecture "sound on the ground"
A clever woman cannot cook without rice, and the efficient operation of software architecture cannot be achieved without hardware support. Keyi Technology takes "self-developed AI edge computing unit (commonly known as" computing box ")" as the distributed core node, combines KVIS cloud training platform and industrial camera data collection to form a "cloud edge end" collaborative system.
KEYETECH's self-developed hardware system - AI edge computing unit and the "Yangtze River" distributed architecture are an indispensable golden partner, which can meet the following requirements:
Horizontal expansion and distributed deployment: multiple AI edge computing units (nodes) are organized into a unified detection network. A node is responsible for the data of one or more cameras, and the "Yangtze River" architecture is responsible for integrating them into a large, scalable system.
Collaboration and division of labor: AI edge computing units focus on reasoning acceleration, while the "Yangtze River" architecture focuses on global tasks, such as summarizing the detection results of all nodes, analyzing yield trends, and uniformly updating AI models.
Elastic scheduling: Based on Linux system and containerization technology, CPU and GPU resources can be dynamically allocated.
Example:
In the visual inspection solution for the plastic packaging industry, KEYETECH has successfully addressed the multiple challenges of extreme inspection conditions and complex on-site environments with the "Yangtze River" distributed software architecture. The system still achieves high-precision defect detection of plastic packaging products 360 ° without dead corners, even in the face of high concurrency data storage peaks generated by products such as lids and bottles, as well as dynamic changes such as frequent changes in production lines and diverse product types.
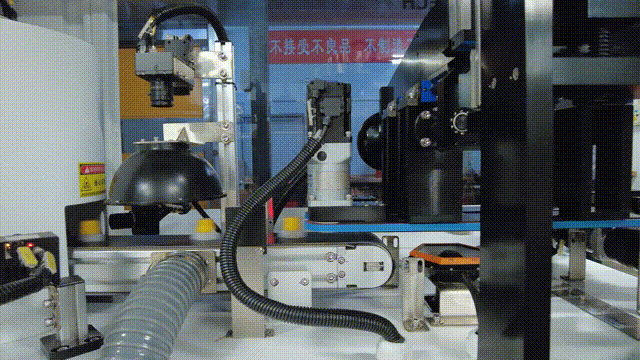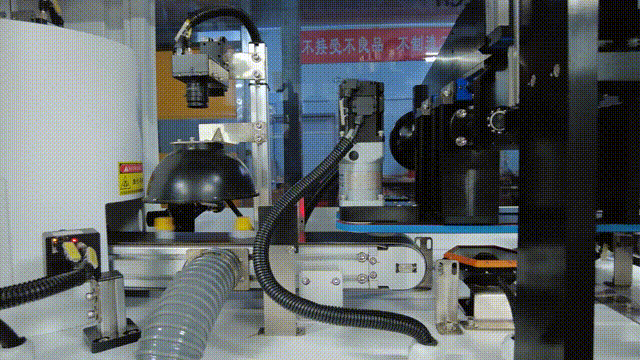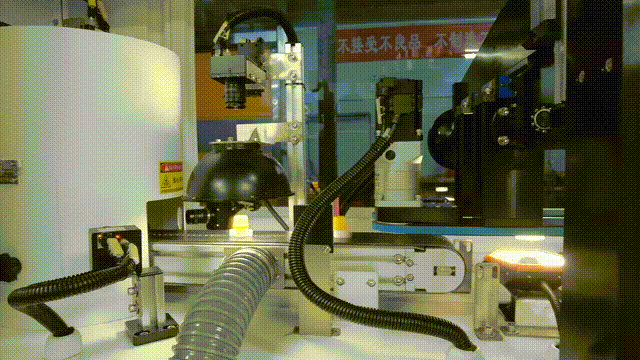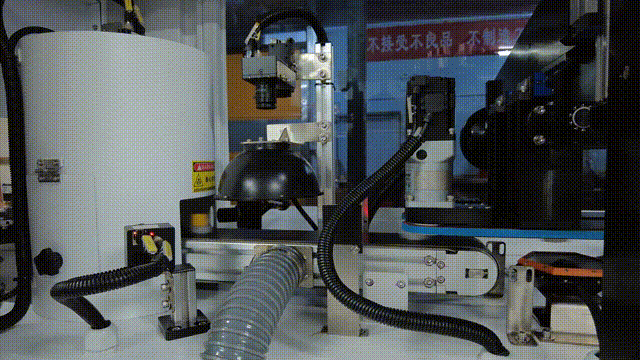
Technical implementation highlights:
Excellent system resilience and scene adaptability
The "Yangtze River" architecture, through dynamic resource scheduling and modular service design, flexibly responds to production line changeover and multi category compatibility requirements, effectively ensuring continuous and stable production under complex working conditions.
Efficient computing power management and peak load capacity
Under continuous high load operation, the system still has sufficient computing power redundancy to cope with data peaks calmly, ensuring uninterrupted detection processes and response without delay.
Real time reasoning and high-precision detection capability
By utilizing distributed parallel processing mechanisms, millisecond level image recognition and defect judgment can be achieved, fully meeting the core requirements of high-speed production lines for real-time quality inspection and accurate discrimination.
The value of the "Yangtze River" distributed software architecture is reflected in:
Unified Resource Management and Scheduling
KEYETECH's "Yangtze River" distributed software architecture is like a "dispatch center" that can remotely monitor the status of all edge nodes (whether they are online, how the load is), deploy software, update AI models, and distribute tasks. It can easily manage hundreds or thousands of detection nodes.
Data Aggregation and Global Analysis
Collect data from all nodes and annotate and model them on the KVIS cloud training platform. From single point issues to system level insights, helping optimize the entire production process and quality control system.
Model Continuous Training and Optimization (MLOps)
This is one of the core values of the "Yangtze River" distributed software architecture. Collect the "difficult cases" (images with inaccurate model judgment) and new defect samples discovered by various edge nodes, and retrain and optimize the model on the powerful computing power in the cloud. The trained new model is seamlessly distributed to all relevant edge nodes through the "Yangtze River" distributed software architecture.
High availability and fault tolerance:
The distributed software architecture of "Yangtze River" is usually designed with redundancy and fault transfer mechanisms. If a management node or data center fails, tasks can be quickly switched to a backup node to ensure that the entire monitoring and management system is not paralyzed.
Not just about 'breaking the deadlock'
It is also the future foundation of AI visual inspection
KEYETECH's "Yangtze River" distributed software architecture fully leverages the data redundancy and disaster recovery capabilities of distributed systems, as well as the efficient acquisition of data from multiple replicas. Through parallel computing, tasks that originally required long computation times are split into multiple tasks for parallel processing, greatly improving computational efficiency.
From "single point limitation" to "global collaboration", the "Yangtze River" distributed software architecture of Keyi Technology is not only a concrete manifestation of technological progress, but also a technological foundation for "cost reduction and efficiency improvement, stability and reliability, and continuous iteration" for the AI intelligent visual inspection industry.




































